The first comprehensive regulation on artificial intelligence in the European Union, the EU AI Act, took effect on August 1 this year. Based on our 15+ years of experience developing complex engineering solutions, we outlined essential information you need to know regarding its impact on your product software development. Keep reading the article for more first-hand insights.
What are the top 5 things I should know about the EU AI Act?
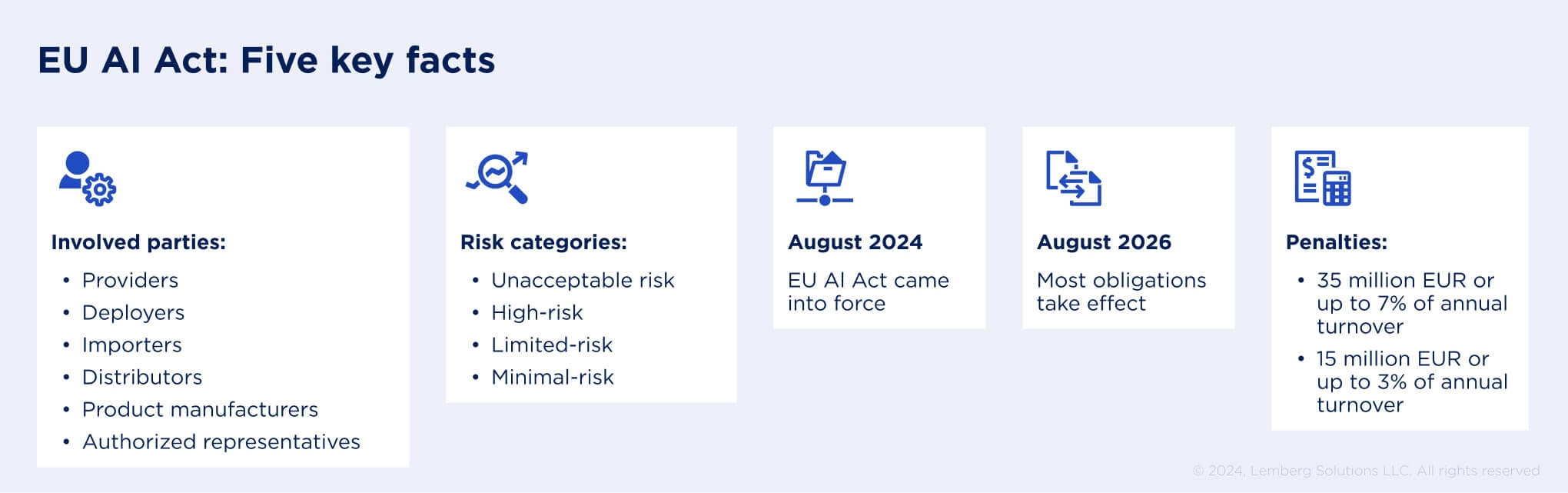
We have put together five facts that you might not come across — take a look:
- The EU AI Act is the first comprehensive European artificial intelligence regulation applicable to all businesses that develop, use, import, distribute, or manufacture AI systems
- It divides applications into four risk categories: those that create unacceptable risk and are forbidden; those that have a high risk and have specific legal requirements; limited-risk applications that require less regulation; and minimal-risk AI systems that go unregulated
- The new Artificial Intelligence Act was enacted in 27 EU Member States on August 1, 2024
- Transition periods for organizations vary depending on the types of AI. On February 2, 2025, obligations related to prohibited AI applications will take effect, while specific obligations will apply to general-purpose AI models from August 2, 2025. However, the majority of obligations under the AI Act will go into effect on August 2, 2026. High-risk systems outlined in Annex I of the AI Act will come into force on August 2, 2027
- And what’s in store for the violators? The answer is simple — those who don’t comply with the AI Act can be fined up to 35 million EUR or 7% of a company's annual turnover; other violations can result in fines of up to 15 million EUR or 3% of an organization’s annual turnover.
What specific changes could the EU AI Act bring to your software development? Let’s explore them further.
Will the EU AI Act impact my current and future product development timeline and budget?
It depends on the type of AI system you use and its classification under the EU AI Act risk categories — minimal, limited, high, or unacceptable. Another essential factor is your role: provider, deployer, importer, distributor, or a combination of these roles.
For example, developing an AI system with limited risk won’t affect your timeline and budget significantly. However, working with high-risk AI systems requires some responsibilities that could slow down or increase your AI development budget. To avoid unexpected shifts in your product creation timeline and budget, leverage our AI development expertise.
AI Act EU responsibilities: What do I need to know?
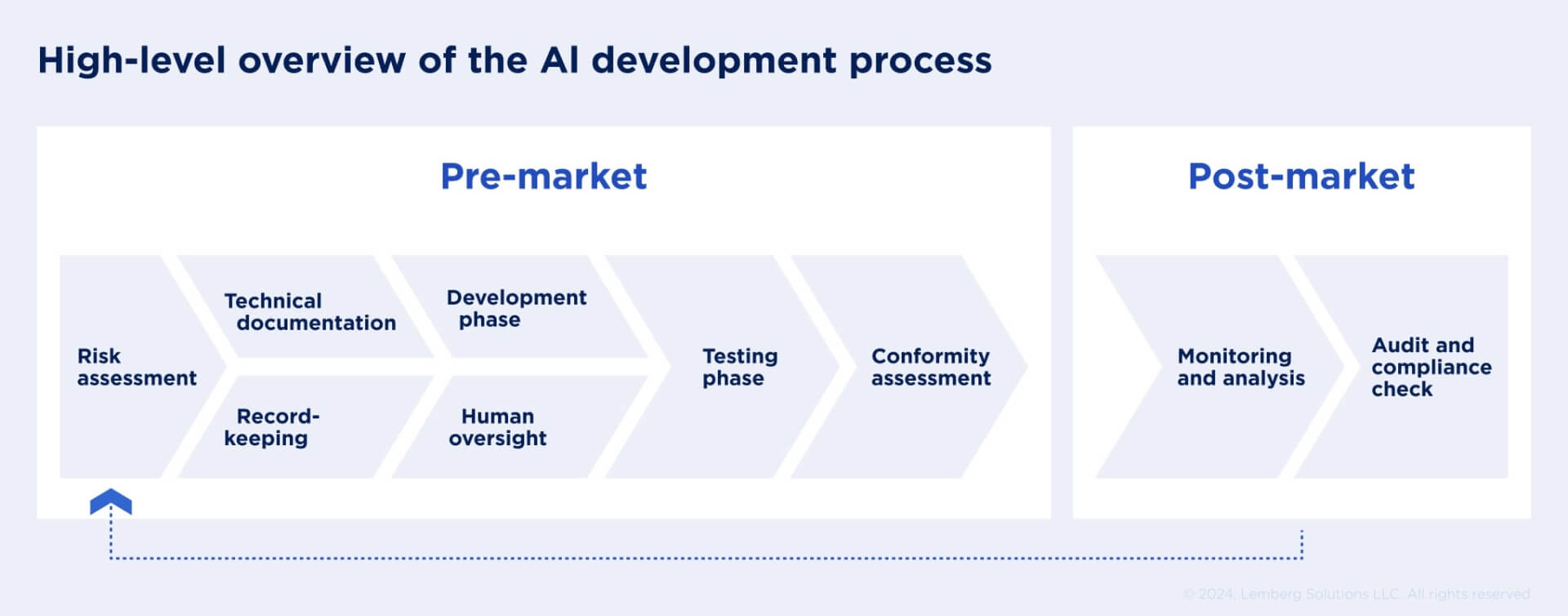
The EU AI Act identifies different roles in the AI value chain, each with its own set of obligations. For example, the provider — responsible for developing AI systems used in their products or/and placing them on the market — has the biggest number of obligations in the development of AI software process.
Below, you can find providers’ main responsibilities related to high-risk AI systems:
- Defining risks and ensuring that you can mitigate and address them
- Assuring the quality of training, validation, and testing data
- Creating technical documentation and keeping it up-to-date
- Enabling certain AI systems to record events over their lifespan automatically
- Making AI systems transparent so users can understand how they function
- Providing human oversight
- Keeping AI systems accurate, robust, and secure.
Providers’ main responsibilities related to limited-risk AI systems:
- Making sure users know they are interacting with artificial intelligence
- Marking AI content identifiable to machines.

Who will conduct the compliance check for the EU AI Act?
National competent authorities will conduct the compliance check for the EU AI Act. These involve a notifying authority and at least one surveillance authority. The appointed authorities in each Member State will monitor the compliance on the development and placement of AI across the EU. The AI Office, a new EU-level regulator, will also oversee and enforce the AI Act EU requirements.
What should I do if I already have a ready-made product with an AI-enabled component?
No worries, if you already have an AI-based component or functionality implemented in your product, simply follow these four steps:
- Determine which EU AI Act risk categories your AI system falls under
- Define your role and your contractors' roles in the AI value chain to understand related responsibilities
- Analyze the risks associated with your AI system and how to mitigate them
- Renegotiate contracts with your AI development company to make sure everything is compliant with the EU AI Act.
You can discover crucial insights about the EU AI Act’s impact on product development in our latest video.
What do sandboxes mean for my product development according to the AI Act EU?
Sandbox enables testing of AI applications in compliant environments to get regulators’ feedback. As a client, you should consider a budget that covers all expenses related to the testing stage. Meanwhile, your AI development company must ensure that test environments are:
- Protected from unauthorized access
- Following regular data backup procedures
- Equipped with fast data recovery plans
- Having procedures and tools for rapid reversal of implementations when needed.
Keep in mind that additional AI regulatory sandboxes may also be set up at regional or local levels or jointly with other countries’ authorities. That’s why you should consider following updates in the specific region where you plan to release your product.
What does a requirement for human oversight mean for my product development?
According to the EU AI Act, high-risk AI systems need effective human oversight during usage to minimize health, safety, and fundamental rights risks. Specialists overseeing the AI system must understand its behavior and technical documentation.
For example, while delivering AI development services, we consistently analyze artificial intelligence output to ensure their relevance. Our data science teams use validation datasets to assess whether the system can effectively make specific choices.
Based on our experience, we recommend to avoid system retraining until a significant number of incorrect choices has been collected. This will help you keep the project within the expected budget and time frames.

How will the EU AI Act affect technical documentation for my product development?
While the AI Act provides a detailed description of technical documentation components, you still need to ensure that it includes every detail related to your AI system.
Check some major things to consider while building your technical documentation:
- Cover a wide range of diverse samples and edge cases, along with defined acceptance criteria at the early discovery stage
- Describe how the system is designed to receive user feedback, keeping in mind reinforcement learning
- Explain how you plan to establish human oversight, depending on the AI system’s potential harm
- Outline the steps to address a certain percentage of your AI system’s errors.
Remember, it’s crucial to begin integrating the AI Act’s requirements into your current documentation as soon as possible, as it might be complex and time-consuming.
How will the EU AI Act impact healthcare development?
Since AI in medical devices won’t be directly regulated by the AI Act, MDR 2017/745 remains the primary regulation. AI will be evaluated as a part of the medical device and its accompanying documents. For providers and their AI development partners, it is important to conduct gap analysis and determine what needs to be added to the current product documentation. For instance, a description of AI in the classification, analysis of potential risks, and data handling.
When choosing an AI development company, how can I determine that it complies with necessary regulations?
Start by reviewing how an AI development company aligns with vital regulatory areas, including data protection and sector-specific standards. For example, inquire whether it complies with ISO 27001:2013, an international data security standard, and ISO 9001:201, a global standard for quality management systems. For healthcare development, your AI development company must comply with ISO 13485:2016, an internationally recognized standard for creating quality management systems for medical device companies.
EU AI Act summary: supporting innovation for trustworthy AI or providing more challenges
As the EU AI Act will come into full effect in 2027, businesses have one to three years to prepare their current and future AI products to meet all regulatory requirements. The new Artificial Intelligence Act introduces categories of risk AI systems and applies obligations to all parties involved in developing, using, importing, or manufacturing them. One major challenge for businesses is effectively integrating new regulatory demands with existing ones throughout development processes.
If you need to make a product that meets all necessary regulations, you are in the right place. As an AI development company with over 15 years of experience, we will help you clarify your concept, navigate through complex requirements, and build a secure, high-quality AI product.







