Are you considering enhancing your device with embedded functionality or building an embedded system from scratch? Keep reading our quick review of five real-life examples of embedded systems we built for our clients. We’ll guide you through five embedded engineering projects in the consumer electronics, agritech, automotive, healthcare, and industrial IoT domains.
Make no stay and keep reading for more insights.
The link below will direct you to a video that provides an in-depth look at five examples of embedded systems, mirroring the content we present in this article.
What are embedded systems and their significance in our daily lives?
Embedded systems are designed to perform specific functions and are composed of hardware components and embedded software. Embedded systems can also be integrated into larger systems and have fixed functionality.
Embedded systems have already transformed our world by seamlessly integrating smart technologies into our daily routines. Embedded systems may have specifically tailored applications like a security system built for a particular company, as well as a wide-ranging application like mobile phones and washing machines.
Embedded systems are applied for thousands of versatile purposes, including industrial machines, consumer electronics, agricultural and processing industry devices, automobiles, medical equipment, and airplanes.

5 Types of Embedded Systems
To help you better understand the types of embedded systems, we outlined five embedded systems examples by industry. Keep reading to get insight into different types of embedded systems.
Automotive embedded systems
Automotive embedded devices are electronic systems integrated into vehicles to control various functions, such as engine management, infotainment, and safety features. These devices ensure uninterrupted real-time performance of automotive operations, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of all types of cars, including electric and hybrid electric vehicles.
If you’re looking to build an automotive embedded device, choose an ASPICE and ISO 26262-compliant tech partner, like Lemberg Solutions. ASPICE ensures your vendor uses best industry practices to meet OEM requirements and detect potential malfunctions early on. ISO 26262 is an international standard regulating automotive electronics development practices, ensuring your automotive product will be built according to high industry standards.
Some of the widely used automotive frameworks are V-model and SAFe model, most often utilized for complex automotive software development projects. Based on Lemberg Solutions' experience, Automotive Grade Linux, Qt, QNX, and AUTOSAR are among the top tools and technologies used while building ECUs, like comfort control modules, power window control units, BMSs, and infotainment systems.
Industrial embedded systems
Industrial embedded systems are specialized units integrated into any kind of industrial equipment to monitor and optimize operations. Industrial embedded devices comprise versatile robotic systems, industrial BMSs, thermostats, industrial gateways, sensors, industrial cameras, etc.
If you’re an equipment manufacturer or a vendor looking for a reliable industrial embedded systems developer, you’re in the right place. Lemberg Solutions delivers custom industrial embedded solutions following all the functional safety and industrial protocols, ensuring high product quality.
Our engineers build industrial embedded systems that are compliant with EtherCAT, Ethernet/IP, PROFIBUS, PROFINET, and other relevant protocols.
Energy embedded systems
Energy embedded devices are specialized systems that optimize energy consumption in industrial and home-based applications. These systems are oftentimes used in renewable energy management, electric vehicles, and smart electrical power networks. Energy embedded systems utilize hardware and software to efficiently control and reduce energy use while ensuring reliability and sustainability.
Some of embedded systems examples for the energy industry are energy storage systems, BMSs, charging stations, EMSs, MPPT trackers for solar panels, energy meters, and power inverters.
If you’re an energy system equipment manufacturer and want to build a robust energy system for your product, find an experienced tech vendor that adheres to all relevant industry standards; this way, you’ll be able to launch a compliant product that can be used accordingly.
Healthcare embedded systems
Healthcare embedded systems extend the functionality of medical equipment by introducing monitoring, diagnostic, and treatment functionality. These systems enable real-time data collection, analysis, and communication, improving patient care and accuracy of medical procedures.
Healthcare embedded systems examples include tonometers, ECG meters, ultrasound machines, cough recognition devices, smart catheters, versatile wearables, nurses, baby monitors, and many more devices that simplify diagnostics and patient care.
When choosing a healthcare embedded systems vendor, check their medical compliances and certifications first. Though many development companies claim they can build a medical system, only a few have all the necessary certifications to develop a market-approved product. At Lemberg Solutions, we hold ISO 13485:2016, ISO 27001:2013, and ISO 9001:2015 certifications. We also comply with HIPAA regulations, IEC 62304:2006, and FDA, ensuring your product is built according to relevant industry standards.
Consumer electronics embedded systems
Consumer electronics embedded systems, such as smartphones, TVs, and other smart appliances, surround us daily. These systems enhance daily end-user operations, improving performance and productivity.
Examples of consumer electronics are limitless — from coffee machines, boilers, thermostats, and climate control equipment to any kind of consumer gadgets and wearables.
If you’re looking to enhance your end users' experiences by building a consumer electronics device, opt for an embedded engineering vendor with versatile experience.
Lemberg Solutions, for one, has experience collecting data for e-bike battery range prediction. As a result, our engineers built an algorithm ensuring users have a highly accurate battery range no matter where their journey takes them.
5 real-life examples of embedded systems
Let’s review five real-life embedded systems examples LS’ embedded engineering team built for our clients from сonsumer electronics, agritech, automotive, healthcare, and industrial IoT domains.
1. Bioprinters for 3D modeling of human organs
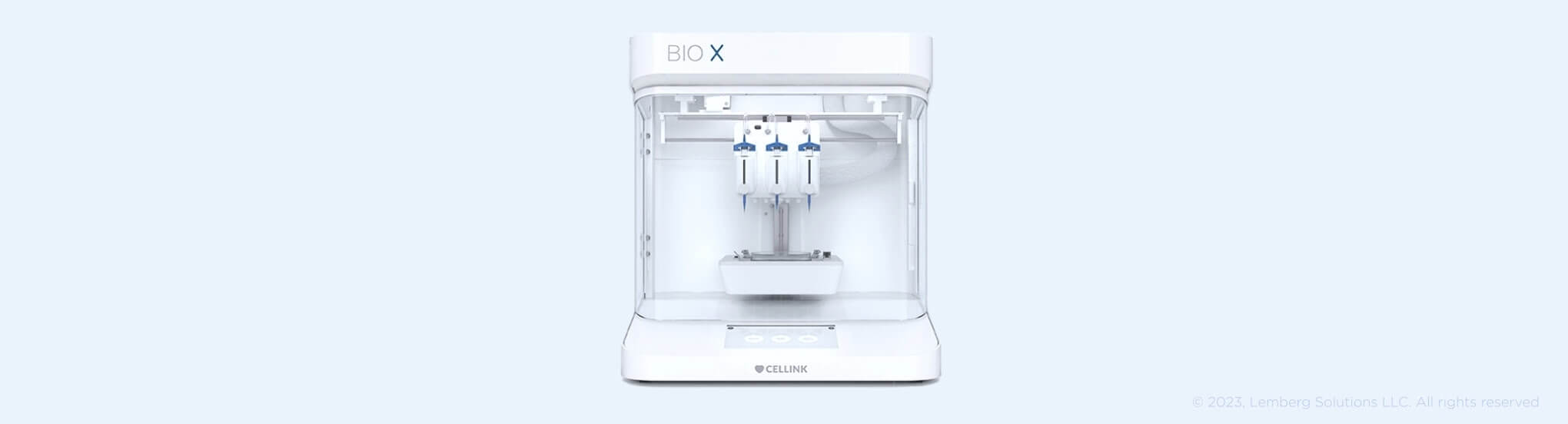

CELLINK is a bioconvergence innovator in developing bioprinters to produce biomaterials. CELLINK combines biology, engineering, and computer science to further the development of bioprinting technologies of the future. This innovative startup promotes the development of such industries as personalized healthcare, cell-cultured food, drugs, and regenerative medicine.
The principle of bioprinter operation is similar to 3D printing. A digital file is used as a blueprint to print an object by layers. The key difference here is that bioprinters print using cells and other biomaterials to build organ-like structures, enabling cells to multiply.
The potential of bioprinting is vast as it can solve such challenges as organ transplantation, regenerative medicine and the reproductive field. Currently, printed organs and tissues are used for pharmacology research to develop safe and effective drugs, avoiding animal and human testing during trials.
Learn about our embedded software development services for CELLINK 3D bioprinters: https://bit.ly/45dVbYq
2. An automated system for pig-weight monitoring

Lemberg Solutions built a first-in-its-kind automated system for pig-weight monitoring that works based on 3D image recognition. Our experts used computer vision and non-iterative neural networks to create this device.
Regular pig weight monitoring is pivotal, enabling farmers to control pigs’ health. However, conventional weight measurement methods are time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially on large farms. That’s why Barkom, a Ukrainian agricultural company, decided to create a solution that would automate daily weight checks.
Our embedded engineering team built an industrial prototype of a pig-weight monitoring device from scratch, including mechanical design, electronics, and the software part.
Find more details about the development of the pigs’ weight measurement device: https://bit.ly/4k6aaeo
3. A battery management system for hybrid electric vehicles and electric vehicles
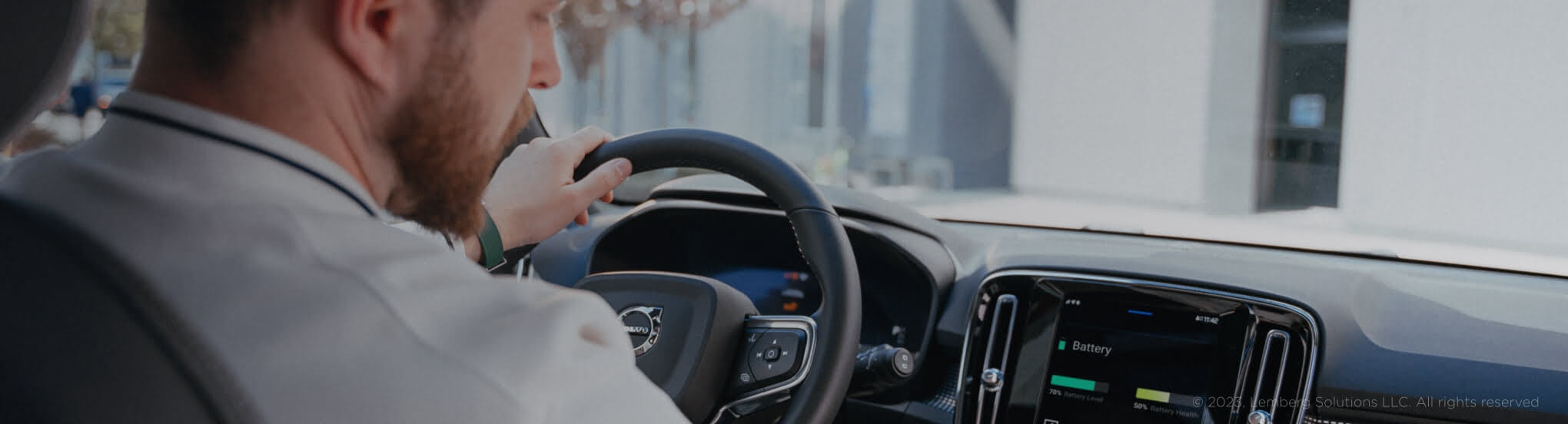

An advanced battery management system built by Lemberg Solutions is real-time embedded system example ensuring the safe operation of the vehicle, correct driving range determination, prolonged battery pack lifespan and reduced risk of fire incidents. The enhanced SoC and SoH algorithms reach 96–98% accuracy by analyzing cell voltage, temperature, current, battery chemistry, and capacity.
Our battery management system conforms to ASIL-D certification. It covers an extensive list of safety features, including Over/Under Voltage, Over/Under Temperature Protection, Short Circuit Detection, Cell Balancing, CAN Communication, and fault handling.
More details on the BMS project: https://bit.ly/3ZP6Fkl
4. A remote digital intensive-care solution

TCC is a provider of a state-of-the-art remote intensive care unit solution. Their device enables hospitals to enhance healthcare services and optimize the workload on intensive care specialists.
Lemberg Solutions’ engineers built an electronic nurse tablet prototype for TCC that measures patients' vitals, including body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen level, and respiratory rate. If the system detects abnormalities that require medical attention, it automatically informs medical staff. The system also generates a therapy and meal plan based on the collected data.
More about the ICU solution we built for TCC: https://bit.ly/3ZBcUrv
5. A BLE-enabled industrial thermostat configured and controlled via mobile apps

Selco develops innovative thermal management products for manufacturing companies in versatile domains like HVAC, food services, medicine, telecommunication, appliances, process controls, and industrial instrumentation.
The device we built is a thermostat with a BLE module controlled by native iOS and Android applications. Our embedded team developed and tested the firmware for the thermostat utilizing the latest BLE chip.
Find out more about the development of electronic thermostats in the case study: https://bit.ly/3ETx6eG
Final word
After reviewing five real-time embedded systems examples, you can decide whether embedded engineering is an optimal solution for your business and tech challenges. An embedded system can control a specific function of your device or perform as an entire operating system, the extent of functionalities only depends on your requirements.
To get a custom consultation on your specific embedded engineering needs, contact us, and our experts will get back to you shortly and provide you with all the answers you need.

FAQ
What is an embedded system?
Embedded systems are designed to perform specific functions within a larger system or device. They consist of hardware and firmware parts. Hardware includes the processor, memory, sensors, modules, etc. Firmware is software built to control hardware operations and perform specific functions. Among the benefits of embedded systems are high efficiency, reliability, low power consumption, and cost-efficiency.
What are examples of simple embedded systems in everyday life?
Simple embedded systems surround us daily — from digital watches, microwave ovens, and remote controls to washing machines, calculators, and thermostats. All of these devices use embedded systems to perform specific tasks and functions, minimizing user interaction.
What are examples of embedded systems projects?
Among embedded systems projects examples we provide in our article are a BLE-enabled industrial thermostat, a remote digital intensive-care solution, a battery management system for hybrid electric vehicles and electric vehicles, an automated system for pig-weight monitoring, and bioprinters for 3D modeling of human organs.