We have written a lot of articles on the location tracking in app development already and many more to come, though we thought that the list will be incomplete without the basics. Below is a short outline to help you learn about GPS accuracy.
What is GPS accuracy?
Accuracy refers to the degree of closeness of the indicated readings to the actual position. The accuracy of GPS results depends on a number of factors:
- Number of channels on the receiver
- Number of satellites in view
- Signal interference caused by buildings
- Mountains and ionospheric disturbances
With the current state of technology, best GPS results are 15 meters accurate (without SA) provided the receiver has a clear shot at a minimum of four satellites.
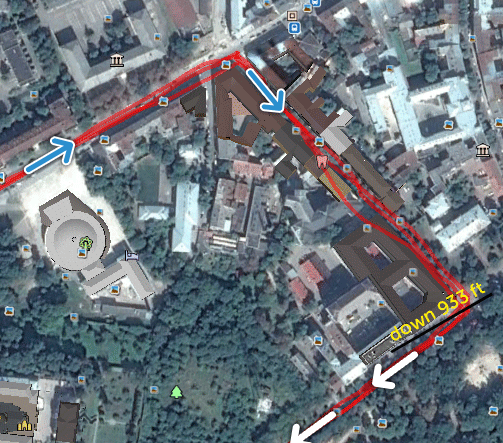
The Global Positioning System (GPS) was originally developed as a military tool. GPS uses satellite technology to find an exact location of user on the Earth. The system does this by using a minimum of three satellites transmitting a signal to an Earth-based receiver. Here is an overview of GPS technology.
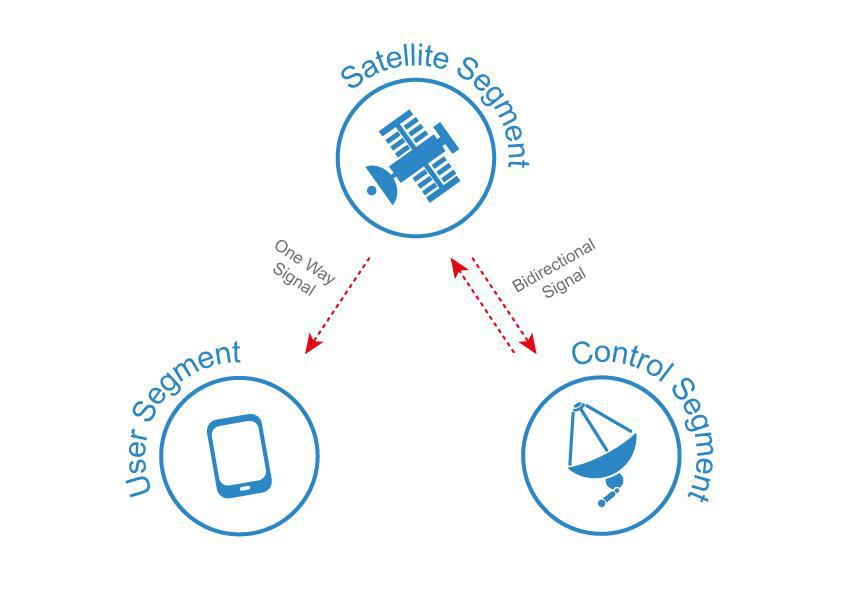
GPS system consists of three major segments:
- Space segment
- Control segment
- User segment
The satellite segment deals with GPS space systems. The control segment corrects positions of satellites and communicates with them for correcting errors and synchronisation. The user segment is presented by many different types of existing GPS receivers and applications for them.
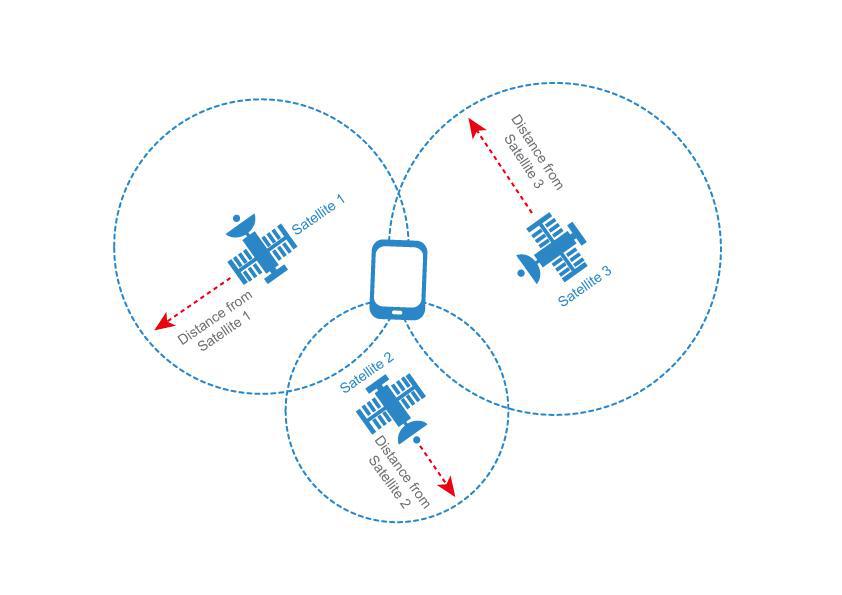
Determining of User position: After receiving all available satellite signals, the receiver compares the time that the satellite sent the signal to the time it was received for each of the available signals. Then calculates the position by comparing the difference between the signals.
Factors That Form GPS Device Accuracy
If in the course of location tracking testing session you get different results on different mobile devices, this does not necessarily mean that there is a problem with the app. It has to do with the GPS receiver of each device having varying accuracy levels. Below is a list of parameters that affect location tracking accuracy:
- Average number of satellites
- Used satellites
- Standard deviation
- Average claimed accuracy (meters)
- Standard deviation of claimed accuracy
- Standard Deviation of Claimed Accuracy as a Percentage of Claimed Accuracy
- Error Change per Satellite Used (metres)
- Correlation Coefficient
In terms of criteria for GPS device selection, please look at the list below:
- Horizontal accuracy – Minimal horizontal accuracy of the target device. Default is 32.8 feet (10 m).
- Vertical accuracy – Accuracy in vertical direction. Default is 98.4 feet (30 m).
- Max response time – Maximal response time in seconds. Default is 1 second.
- Power consumption – Determines how much power should device use. This way, high power devices can be restricted. Default is No requirement.
- Altitude required – Determines if the altitude is required. Default is true.
- Speed and course – Determines if speed or course are required. Default is true.
Summary
So you now know what GPS accuracy means and what are the key factors that influence it.
Lemberg is always here to help, so don`t hesitate to contact us or add your questions in the comment section below.

