The worldwide market for data loggers across various sectors is projected to grow to $46.58 billion by 2036, compared to $9 billion this year. Moreover, energy, transportation and logistics, manufacturing, and automotive industries prioritize IoT-powered connectivity and cloud-based storage to collect and store data efficiently and securely.
In this article, we cover the role of a data logger, the types of data loggers, and how to use a data logger to improve your data collection process so you can decide on the best match for your business goals.
What is a data logger?
A data logger is a small device integrated with sensors that can collect, record, and store data, including environmental like temperature, humidity, or pH, vehicle telemetry, and video frame during a certain time period or in real time.
There is a wide range of data logger applications in different industries, including collecting environmental data and monitoring industrial processes, logistics, battery energy, and energy storage systems management.
How does a data logger work?
A data logger with a built-in microprocessor uses sensors and internal memory to collect and store environmental data and send it to the cloud. A considerable benefit of data logger development is in their reliability, meaning these devices provide long-term monitoring of your system or equipment.
To let you monitor the data collection process, data loggers can be connected to a computer, sending the data to software app storage. Alternatively, they can be IoT-powered, sending data wirelessly through an IoT gateway.
The more sensors you integrate into the data logger, the more types of data you can collect and store, as data loggers can process a large number of inputs. These options depend on your project requirements and the purpose of your data logger development.

Data logger device: core components
Despite data loggers' uses and types, these devices have similar components, ensuring their stable operation. Let's further define what components the data logger consists of and what a data logger does.
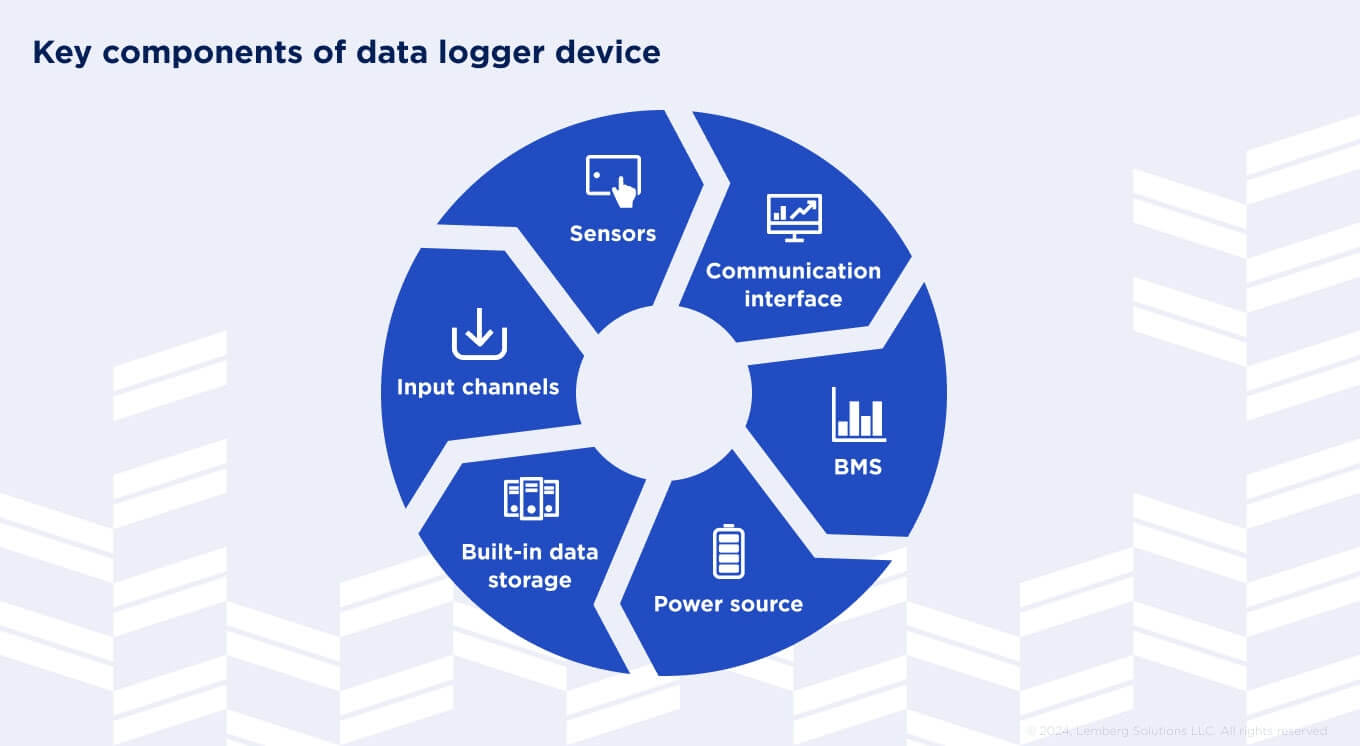
Sensors
Sensors integrated into the data logger enclosure collect accurate data, including temperature, humidity, power, voltage, and pressure. Typically, one sensor collects one parameter, but integrated sensors can also have complex usage depending on the data logger's goal.
Data logger development can follow a sensor fusion approach to improve data collection for multiple sensors and unite them into a comprehensive picture.
Input channels
Input channels are connectors between sensors and data logger device hardware. Each input channel is connected to a specific sensor that collects certain types of digital signals, which are available for recording, reading, and storing.
Built-in data storage
To save the collected data, data loggers have integrated storage to save the required data. Depending on your requirements, these storages can vary from memory chips and SD cards to USB drives.
Power source
Batteries or external sources commonly power a data logger device. Despite external sources commonly having backups, batteries are considered a more reliable way to supply power uninterruptedly, as you can monitor their conditions and foresee their replacement or charging.
Batteries also provide mobility for data-logging devices, so you can place them anywhere you need and still have a great connection and uninterrupted data collection.
Communication interface
There are two primary types of communication interfaces – wired and wireless. A communication interface allows you to monitor the collected data remotely through your devices in real time.
The integration of wireless connectivity through 4G/LTE, NB-IoT, LoRa, WiFi, or BLE makes your data loggers IoT-powered. All stored data is immediately transferred to the software connected to your device, enabling you to monitor the data visualization, analyze it quickly, and, as a result, make data-driven decisions.
Types of data loggers
As mentioned above, data loggers have applications in diverse sectors, as they can collect one or several data types at once.
Further, we will explore the different types of data loggers, the options they provide, and how they differ.

Energy data loggers
Energy data loggers monitor equipment performance and power usage, including current and voltage, track peak energy use periods, and calculate consumption.
This type of data logger provides many insights into device power use, managing batteries and their conditions to make battery range predictions, prevent breakdowns, and fix issues on time. It also helps businesses define the operations that consume the most energy, determine the areas of excessive power usage, and, as a result, fix consumption inefficiencies.
Data loggers for solar/PV systems
Solar or PV data loggers allow you to monitor your solar system remotely in real time, collecting all necessary operation data, including power generation, temperature, voltage, and other required metrics.
Integrated sensors enable data loggers to collect and transmit all this data to the application's local storage or the cloud over the internet in a readable format. Thus, you can track the systems' operation in the fields, assess their performance and efficiency, identify issues and abnormalities, and prevent equipment breakdown.
Automotive data loggers
Data loggers are widely used in the automotive industry for vehicle real-time data collection, ensuring drivers' safety and assistance. The devices collect data from the vehicle's networks to monitor its real-time operation, identify issues early, and fix them promptly.
This type of data logger usually has local storage for transmitting metrics like temperatures, brake settings, RPM, fuel efficiency, location, and speed from vehicles. It can also be integrated with data pre-processing to detect deviations or abnormalities immediately.
Data loggers for equipment monitoring
Data loggers can also assist you in monitoring equipment performance remotely, ensuring continuous maintenance, and providing up-to-date information on its conditions. The parameters data loggers collect are based on your machine specifics and end goals.
Properly calibrated data loggers placed near or directly on each device provide preventive maintenance, detecting abnormalities in the early stage or identifying potential issues that may occur based on collected metrics.
Environmental data loggers
Environmental data loggers collect such indexes as temperature, humidity, illumination level, and other conditions directly from the location of your device. One data logging device can collect one data type as well as various indicators through integrated sensors.
There are several types of environmental data loggers, including temperature and humidity data loggers:
- Temperature data logger
Temperature is the core and the most widespread index measured by data loggers. Monitoring the heat in industrial machinery, batteries, or energy storage systems is crucial to prevent equipment breakdown and ensure safe work conditions for employees. In this case, data loggers also help monitor whether the temperature complies with the industrial regulations and standards.
- Humidity data logger
Humidity data loggers collect data in sensitive environments using integrated sensors. They can be used for home, like monitoring humidity in basements and attics, as well as in warehouses, greenhouses, and other environments where tracking moisture and detecting abnormalities is crucial.
4 benefits of data logger development
A data logger is an efficient and quick way to collect data about environmental conditions and devices remotely. Let's see what benefits data logger development can introduce to your business processes, regardless of your industry.
1. Automated process of data collection
A data logger enables automated data collection from locations and environments that should be monitored 24/7. It also ensures the accuracy of collected data, avoiding missing any elements or parameters as could be the case with manual collection.
2. Real-time monitoring
As data loggers have applications in many industries for different purposes, you may not always have constant, quick access to the devices that need to be monitored. Setting up a data logger provides real-time device monitoring and alerts in case of abnormalities or breakdowns.
3. Safety
Data loggers provide real-time and constant monitoring of remote equipment and its conditions. If something is going wrong, like a considerable temperature change or power outage, you are immediately notified and can make decisions before these changes harm the devices' operation.
4. Integration with other systems
Connecting a data logger with your existing systems, like energy management, battery management, or manufacturing monitoring software, lets you analyze the received data in real time, gain insights into the devices’ state of health and environmental conditions, record historical data to determine patterns and trends for predictive maintenance and improved forecasting.
Real-life examples in different industries
We have a strong track record in developing and updating data-logging devices for various industries. Keep reading as we share some real-life examples of data loggers we built for energy, transportation and logistics, and healthcare industry businesses.
Energy
Our latest client success story is the development of IoT data loggers for energy storage systems created by Voltfang. Our client, Voltfang, is a Germany-based company that produces stationary energy storage systems incorporating second-life batteries. They aim to develop energy sustainability and provide customers with long-term and environmentally safe solutions.

Our embedded engineering team got a task to develop an IoT-powered device to let our client collect data from battery management systems within the energy storage systems their company produces. First, we offered improvements to the solution architecture design, developed firmware, and integrated AWS cloud services to store data from BMS.
Get more insights about the development process at the link.
Transportation & logistics
As an example of a data logger application in the transportation and logistics industry, we want to share our collaboration with Konvoi.
Konvoi, a Germany-based company, produces truck security devices that help drivers protect their vehicles against theft, damage, and attacks. Initially, they had IoT data loggers that vehicles should set up to monitor, collect, and store real-time data in the cloud.

However, they struggled with the firmware code integrated into their device, as they wanted to make it more efficient for their customers. Thus, our embedded engineers needed to perform a comprehensive code audit and recommend improving it. Learn what steps the firmware audit process comprised and what results our team delivered.
Healthcare
The following case of developing a data logging device is a hygiene monitoring and activity tracking system for Barkom. This is an agriculture company based in Ukraine that raises livestock and sells food products of its production.

As our client’s company prioritizes safety, they wanted to ensure the highest protection from pests and germs on the farm. That's why they requested to automate staff hygiene monitoring to improve the existing biosafety procedures using smartwatches that collect and store accelerometer data. Find out more about the development stages and what challenges we had to resolve while building a solution for Barkom.

How to choose a data logger type for your project
Once you decide to build a data logger, it is vital to define your final goal and learn what type of data you need to collect, what time period it should last, and what happens next after the data gets stored. This will simplify the choice of data logger type and functionalities to meet your requirements, whether you need it for soil moisture management, power consumption monitoring, battery management, or temperature tracking.
The data logger type, features, and major components will ultimately depend on your business and industry specifics, including industry-related compliance and regulations.
Entrust your data logger development project to our embedded experts, who will help you define the core requirements, provide solution architecture design, and develop it.





